Mapping your network is vitally important for keeping on top of how it’s performing, as well as for pinpointing bottlenecks or network issues, and troubleshooting problems. But approaching this process manually with a large or complex network can quickly become overwhelming.
May 26, 2021 Here is our list of the best network mapping and topology software: SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper EDITOR’S CHOICE Automatic and on-demand network topology mapping options that can also record VMWare and Hyper-V virtualizations. Auto-detects all updates and changes to your network in real-time. Logical network map: A logical network map details the logical connections between devices on a network. For example, a logical network map might visualize the Layer 2 and Layer 3 connections that enable data to flow from a server to a default gateway such as a firewall, and then the internet.
Nmap ('Network Mapper') is a free and open source utility for network discovery and security auditing. Many systems and network administrators also find it useful for tasks such as network inventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime. Here is our list of the best network discovery tools and software: SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor EDITOR’S CHOICE Offers automatic discovery and mapping of networks, including remote sites, cloud-based services, and wifi systems. The wireless network heat map shows the overlap of wifi signals and dead zones.
I’ve found using a network mapping tool is a much better approach—especially if it can map your network for you automatically. There are a number of quality tools on the market, paid and free, which I’ll go into after a review of the network mapping process. For top-line solutions I recommend SolarWinds® Network Performance Monitor and Network Topology Mapper, both easy-to-use tools capable of mapping your network along with providing important data and performance metrics.
What Are Network Maps?
There are two main levels of maps to consider: physical and logical. While open-source network mapping tools can create a physical network map, they may not offer automated scanning to ensure the map is always up to date.
There are three levels of maps to consider—physical, logical, and functional.
A physical network map diagrams all the actual components of your network, including cords, plugs, racks, ports, servers, cables, and more. A physical network map gives you a visual representation of all the material elements of your network and the connections between them.
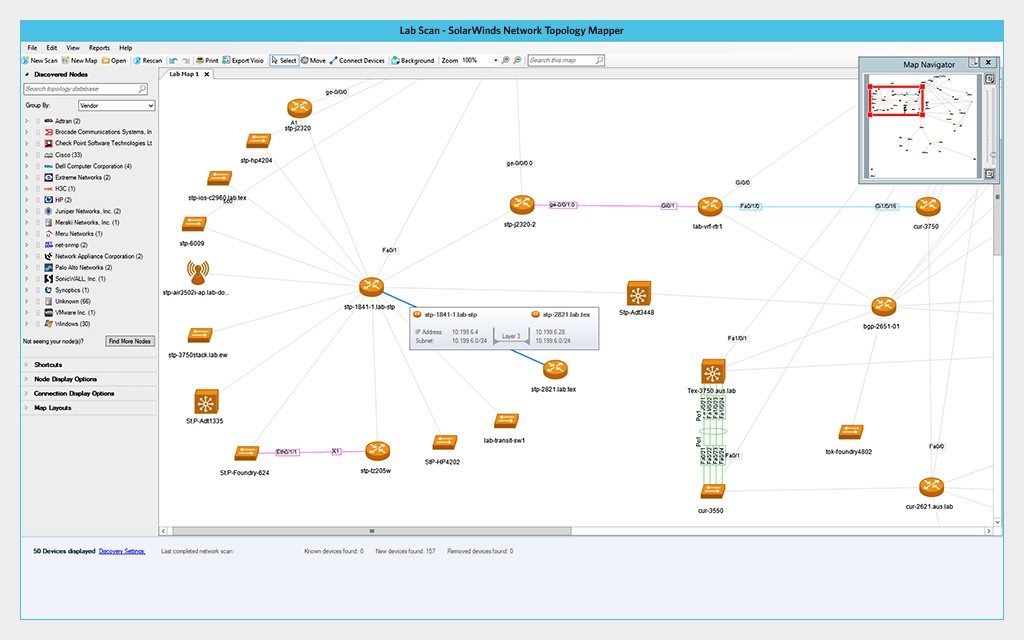
A logical map is more abstract than the physical network map. It shows the type of network topology (bus, ring, etc.), and how the data flows between the physical objects in your network. This includes IP addresses, firewalls, routers, subnets and subnet masks, traffic flow, voice gateways, and other segments of the network.
To note: Since logical and physical network maps depict the same network environment from two different perspectives, it’s best to use both types to get a more comprehensive look at your network.
A functional network map shows you how application traffic flows through the network physically. These types of network maps are only as useful as they are accurate, which means you need an appropriate and high-quality tool.
Best Network Mapper Download
How Does Network Mapping Work?
Network mapping is the process of visualizing all the devices on your network, how they’re connected, and how the overall network is structured. The network map generally equips you with information about whether the network is functioning properly or whether any particular device has a problem.
Networks are set up in different structures, also called topologies. The structure can have a major effect on how your network functions, what happens when a device or server goes down, and how complex it is to manage. When you map your network, you’re basically mapping its topology into a visual network diagram.
Here are the main network topologies to be aware of:
- Bus – A bus network is set up in a straight line, allowing data to flow through the network from the server to each node one by one
- Ring – In a ring, network the nodes are arranged in a circle, and data can flow around the circle in one or both directions
- Tree – In a tree topology, a server has multiple branches of nodes coming off it. This is a bit more robust than a bus or ring topology, as with a tree topology, if one of the branches has a problem with a node, the rest of the network will still function. With ring and bus topologies, a problem with one node can cause the whole network to go down
- Star – A star topology has one central node with all others coming off it in a star pattern
- Mesh – A mesh network has connections between all the nodes and servers, like a lattice or mesh. It has high failover protection because if one node goes down, the network can reroute the data to get it where it needs to go
- Hybrid – A hybrid topology is simply a combination of any or all the above network structures and is very common as networks get larger

Best Network Mappers
Of course, all these types of network maps are only as useful as they are accurate, which means you need an appropriate and high-quality tool. While mapping can be done manually using tools like ping and tracert, followed by a visual mapping or vector program, this process can be prohibitively time-consuming. Similarly, if you’re considering a free network mapping solution, you should check which kind of network map it offers and whether it will give you the full visibility you need to optimize network performance.
Below, I look at some of the best network mappers on the market and what makes them stand out from the pack.
- Network Performance Monitor – Free Trial
My top pick is SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM). NPM is extremely useful for both mapping networks and determining how your network is performing. It includes a feature called NetPath, which maps your network and then provides you with information on network performance, traffic, and configuration along the entire service delivery path. You can also see performance metrics with hop-by-hop data between your central servers and your satellite offices.
NPM also features a number of network visualization graphs and charts. Insights from NPM network mapping features can easily be viewed alongside your other performance tools to provide troubleshooting assistance of your entire network. Try out a free trial of NPM for 30 days.
- Network Topology Mapper – Free Trial
SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (NTM) is focused on network mapping. Unlike NPM, the tool doesn’t include network performance measurement capabilities. However, NTM shines in its ability to automatically plot your network to build multiple different kinds of network maps from a single scan.
The automatic scanning function is useful if you have an already established network needing to be properly mapped. It automatically detects any changes in your network topology and updates the maps accordingly. You can choose whether you want it to determine your network using SNMP, ICMP, WMI, CDP, or another method of discovery. You can also try NTM free for up to 14 days.
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is a well-known software with monitoring and performance tools as well as reporting features and dashboards. It lets you create maps to show you devices and connections, as well as live status information for your network, so you can detect problems in one glance and troubleshoot effectively using maps as a primary source of information. You can customize your map using HTML, and you can share the map with whoever you want (company-only or external). While the maps are extremely useful, you must create them manually using the drag-and-drop map editor, which can be time-consuming.
Device42 is a configuration management database with auto-discovery and application mapping tools. You can set up a schedule and Device42 will automatically scan your network and infrastructure and detect any changes as they’re made, so your network information is always up to date. It can track IP and non-IP based devices and assets, hardware, software, and interdependencies between devices, as well as resource utilization. You can also generate dependency and impact visuals using the Device42 NetFlow collector, which allows you to view topologies at different levels. Overall this is useful software, but the auto-discovery can be difficult to implement if the network is very complex, as it tends to pick up unnecessary information.
Intermapper allows you to create custom maps quickly and effectively, automatically mapping all the IP-enabled devices in your network. You can customize your maps with colors and different background options, as well as color-coded statuses to show you how the network is performing. It provides you with real-time text or email alerts if there are any issues, helping prevent your users from being affected. Intermapper works for Mac, Linux, and Windows, and offers a 30-day trial, a free version, and an enterprise version.
Nmap is a free and open-source network mapping tool that uses IP packets to determine what hosts are on the network, what services are offered by those hosts, and identify operating systems, firewalls, and other information. It runs on Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X, and can link in with other Nmap suite tools including Zenmap, Ncat, Ndiff, and Nping. Nmap comes with a learning curve, but it’s a great option if you’re working with a small business without the budget for a professional tool.
Spiceworks is a manual network mapping tool that allows you to view an interactive network diagram of how your devices work together and relate to each other. You can add, edit, move, and resize devices on the map to show how your network is structured, as well as using filters and views to show only the most important data. The network map displays lines between each node—the thicker the line, the more bandwidth is being used. However, the mapping is manual, which means you need to redo your network map every time your network changes. The Spiceworks network mapper is free, though, so it’s a good choice for someone who has the time to map a smaller, less complex network rather than a changing enterprise system.
Best Network Mapping Solution
There are a number of good network map tools on the market, but in my view, some are better equipped to handle the task than others. Some are tools you can use to help you map the network yourself. Others look at your network and map it automatically. Automatic network mappers result in fewer mistakes and missed devices, and are designed to adapt when a new server or node is added to the network. I recommend trying Network Performance Monitor as an all-in-one network map and performance tool for any size environment.
Recommended Reading
Best Network Monitoring Software – If you need to do more than map your network, look into a complete network monitoring solution. I’ve written reviews of what I consider to be the best network monitoring software.
6 Best FREE Patch Management Software – Network maintenance involves more than monitoring the topology—you need to make sure you’re keeping on top of all your patches and updates, among other priorities. There are a number of free patch management solutions that can help you. Here are my top picks.
| ||||||||||||||||

- Nmap 7.90 has been released with Npcap 1.00 along with dozens of other performance improvements, bug fixes, and feature enhancements! [Release Announcement | Download page]
- After more than 7 years of development and 170 public pre-releases, we're delighted to announce Npcap version 1.00! [Release Announcement | Download page]
- Nmap 7.80 was released for DEFCON 27! [release notes | download]
- Nmap turned 20 years old on September 1, 2017! Celebrate by reading the original Phrack #51 article. #Nmap20!
- Nmap 7.50 is now available! [release notes | download]
- Nmap 7 is now available! [release notes | download]
- We're pleased to release our new and Improved Icons of the Web project—a 5-gigapixel interactive collage of the top million sites on the Internet!
- Nmap has been discovered in two new movies! It's used to hack Matt Damon's brain in Elysium and also to launch nuclear missiles in G.I. Joe: Retaliation!
- We're delighted to announce Nmap 6.40 with 14 new NSE scripts, hundreds of new OS and version detection signatures, and many great new features! [Announcement/Details], [Download Site]
- We just released Nmap 6.25 with 85 new NSE scripts, performance improvements, better OS/version detection, and more! [Announcement/Details], [Download Site]
- Any release as big as Nmap 6 is bound to uncover a few bugs. We've now fixed them with Nmap 6.01!
- Nmap 6 is now available! [release notes | download]
- The security community has spoken! 3,000 of you shared favorite security tools for our relaunched SecTools.Org. It is sort of like Yelp for security tools. Are you familiar with all of the 49 new tools in this edition?
- Nmap 5.50 Released: Now with Gopher protocol support! Our first stable release in a year includes 177 NSE scripts, 2,982 OS fingerprints, and 7,319 version detection signatures. Release focuses were the Nmap Scripting Engine, performance, Zenmap GUI, and the Nping packet analysis tool. [Download page | Release notes]
- Those who missed Defcon can now watch Fyodor and David Fifield demonstrate the power of the Nmap Scripting Engine. They give an overview of NSE, use it to explore Microsoft's global network, write an NSE script from scratch, and hack a webcam--all in 38 minutes! (Presentation video)
- Icons of the Web: explore favicons for the top million web sites with our new poster and online viewer.
- We're delighted to announce the immediate, free availability of the Nmap Security Scanner version 5.00. Don't miss the top 5 improvements in Nmap 5.
- After years of effort, we are delighted to release Nmap Network Scanning: The Official Nmap Project Guide to Network Discovery and Security Scanning!
- We now have an active Nmap Facebook page and Twitter feed to augment the mailing lists. All of these options offer RSS feeds as well.
Nmap ('Network Mapper') is a free and open source(license) utility fornetwork discovery and security auditing. Many systems and networkadministrators also find it useful for tasks such as networkinventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host orservice uptime. Nmap uses raw IP packets in novel ways to determinewhat hosts are available on the network, what services (applicationname and version) those hosts are offering, what operating systems(and OS versions) they are running, what type of packetfilters/firewalls are in use, and dozens of other characteristics. Itwas designed to rapidly scan large networks, but works fine againstsingle hosts. Nmap runs on all major computer operating systems, andofficial binary packages are available for Linux, Windows, and Mac OSX. In addition to the classic command-line Nmap executable, the Nmapsuite includes an advanced GUI and results viewer(Zenmap), a flexible datatransfer, redirection, and debugging tool(Ncat), a utility forcomparing scan results (Ndiff), and a packet generation and response analysis tool (Nping).
Nmap was named “Security Product of the Year” by LinuxJournal, Info World, LinuxQuestions.Org, and Codetalker Digest. Itwas even featured in twelvemovies, includingThe Matrix Reloaded,Die Hard 4,Girl With the Dragon Tattoo, andThe Bourne Ultimatum.
Best Network Mapper Download
Nmap is ...
- Flexible: Supports dozens of advanced techniques formapping out networks filled with IP filters, firewalls, routers, andother obstacles. This includes many port scanning mechanisms (both TCP &UDP), OSdetection, version detection, ping sweeps, and more. See the documentation page.
- Powerful: Nmap has been used to scan huge networks ofliterally hundreds of thousands of machines.
- Portable: Most operating systems are supported, includingLinux,Microsoft Windows,FreeBSD,OpenBSD,Solaris,IRIX,Mac OS X,HP-UX,NetBSD,Sun OS,Amiga,and more.
- Easy: While Nmap offers a rich set of advanced features forpower users, you can start out as simply as 'nmap -v -A targethost'. Both traditional command line and graphical (GUI)versions are available to suit your preference. Binaries areavailable for those who do not wish to compile Nmap from source.
- Free: The primary goals of the Nmap Project is to help makethe Internet a little more secure and to provideadministrators/auditors/hackers with an advanced tool for exploringtheir networks. Nmap is available for free download, and also comes with fullsource code that you may modify and redistribute under the terms ofthe license.
- Well Documented: Significant effort has been put intocomprehensive and up-to-date man pages, whitepapers, tutorials, andeven a whole book! Find them in multiplelanguages here.
- Supported: While Nmap comes with no warranty, it is well supported by a vibrant community of developers and users. Most of this interaction occurs on the Nmap mailing lists. Most bug reports and questions should be sent to the nmap-dev list, but only after you read the guidelines. We recommend that all users subscribe to the low-traffic nmap-hackers announcement list. You can also find Nmap on Facebook and Twitter. For real-time chat, join the #nmap channel on Freenode or EFNet.
- Acclaimed: Nmap has won numerous awards, including'Information Security Product of the Year' by Linux Journal, InfoWorld and Codetalker Digest. It has been featured in hundreds ofmagazine articles, several movies, dozens of books, and one comic bookseries. Visit the press pagefor further details.
- Popular: Thousands of people download Nmap every day, andit is included with many operating systems (Redhat Linux, DebianLinux, Gentoo, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, etc). It is among the top ten (out of30,000) programs at the Freshmeat.Net repository. This is importantbecause it lends Nmap its vibrant development and user supportcommunities.
Nmap users are encouraged to subscribe to the Nmap-hackersmailing list. It is a low volume (6 posts in 2017), moderated listfor the most important announcements about Nmap, Insecure.org, andrelated projects. You can join more than 128,000 current subscribersby submitting your email address here:
We also have a development list for more hardcore members(especially programmers) who are interested in helping the project byhelping with coding, testing, feature ideas, etc. New (test/beta)versions of Nmap are sometimes released here prior to generalavailability for QA purposes. You can subscribe at the Nmap-dev listinfo page.
Both lists are archived (along with many other security lists) at Seclists.org.
Best Network Mapper

Though it isn't nearly as active as the mailing lists, the official IRC channel is #nmap on Freenode (irc.freenode.net).
| Intro | Reference Guide | Book | Install Guide |
| Download | Changelog | Zenmap GUI | Docs |
| Bug Reports | OS Detection | Propaganda | Related Projects |
| In the Movies | In the News | ||